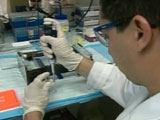
Now, scientists and researchers can use information from the Human Genome Project (HGP) to have a better understanding of the disease so we can figure out what is causing the disease and learn how to efficiently treat it.
Gene Testing
What is it? It allows scientists to scan and identify mutated genes. Therefore, researchers can know exactly what to treat and what would actually work. Also, disease prevention and survival rates would increase. Even though, an invasion of privacy is the one negative outcome, because the testing is targeted at healthy patients that may carry the mutated genes, but not necessarily activate the disease. (4a) |
Gene Therapy
What is it? It corrects the mutated genes that may cause diseases. How is it used?
(4b) | 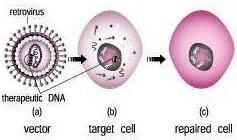 This technique are carried out by using vectors to insert the genes. Vectors are usually viruses. |
Medications
Unfortunately, there is no cure for Alzheimer's disease just yet. So far, doctors are prescribing drugs that will only slow down the disease.
Two drugs have proven to work:
Cholinesterase inhibitors [donepezil (Aricept), rivastigmine (Exelon) and galantamine (Razadyne)]
It improves the levels of neurotransmitters in the brain. Unfortunately, cholinesterase inhibitors do not work for everyone, because only half the patients show improvements. Side effects include diarrhea, nausea and vomiting. (4c) |
Memantine (Namenda)