Before we go into detail. It is important to understand the basics of gene expression and the role of Ribonucleic acid (RNA).
Introduction to RNA
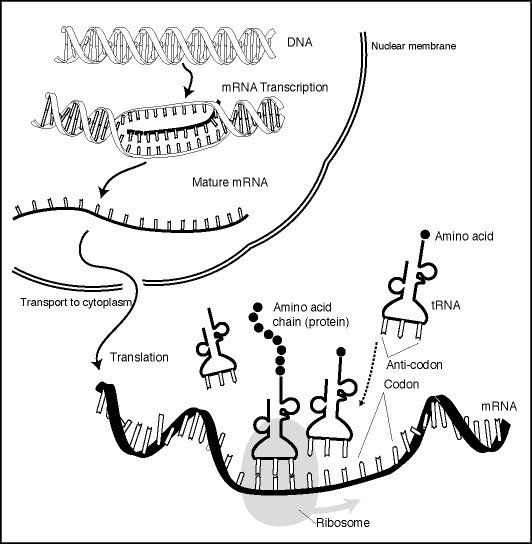
Take a look at the diagram to the left. The steps: 1. DNA is transcribed by an RNA polymerase. 2. The RNA is created. 3. The RNA goes through "splicing" and the exons join together to become the messenger RNA (mRNA). *This is not shown in the diagram. 4. The mature mRNA leaves the cell through one of the nuclear pores. 5. Now, the process of translation begins. 6. The ribosome goes down the mRNA and 'reads' it. 7. Transfer RNA (tRNA) matches up to the mRNA (codons and anti codons). The tRNA caries amino acids and drops it off to the ribosome. 8. The ribosome connects the amino acids and the chain becomes a protein when the translation process stops. |
Alright! Since you have learned, or refreshed your mind, about gene transcription and translation, lets see how that knowledge helped scientists apply it to Alzheimer's Disease.
Beyond the Basics:
RNA Interference (RNAi)
What is RNAi?
CLICK HERE for an animated slide show. A brief overview:
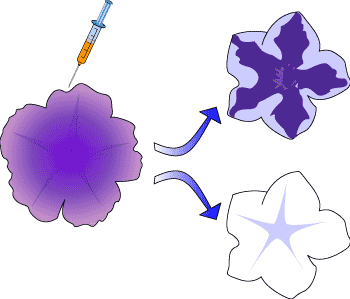
Well, good question. With the possibility of elimination certain genes, we can start regulating diseases. For example, Alzheimer's disease can be detected and silenced so the gene would not be expressed in the future. The Discovery: The production of small interfering RNA (siRNA) was used to see if it can silence a well-characterized tau mutation (V337M) and the amyloid persecutor protein mutation (APPsw). Then, using that process as a template, they created short hairpin RNA (shRNA) plasmids that successfully silenced mutant tau or APP alleles. (5b) | Within an experiment, researchers wanted to make a purple petunia 'more purple'. So, they cut off a gene that contains 'purple dye' and inserted it into the petunia. Surprisingly, the results did not come out as expected. Instead, the petunia lost its color! This experiment led to the discovery of RNAi and its very important function. |
MicroRNA
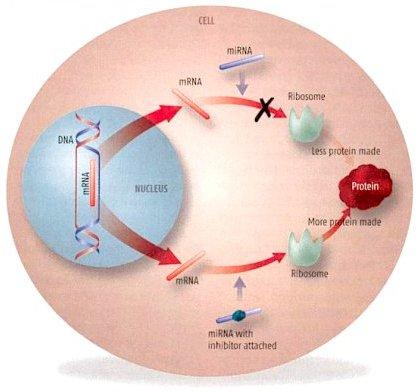
What is microRNA? "MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small regulatory RNAs that participate in posttranscriptional gene regulation in a sequence-specific manner." (5c)
Within an experiment, changes in microRNA (miRNA) expression profiles of patients afflicted with Alzheimer's were examined. As it turns out, several miRNAs potentially involved in the regulation of APP (amyloid precursor protein) and BACE expression appeared to decrease in diseased brain. Also, miR-29a, -29b-1, and -9 can regulate BACE expression. Therefore, less of the APP and BACE genes would be expressed within the patients. (5d) |
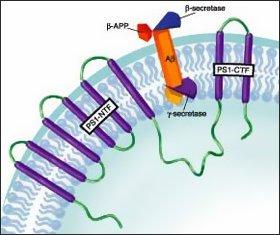
What is Beta-secretase (BACE)? |
RNAi vs. microRNA
A study (using mice as protocols) showed that large amounts of shRNA blocked the cell's ability to export microRNA, which uses the same export pathway. The mice died without normal functioning of microRNA. (5f)
Further studies are being made to prevent the blockage from happening.