To start off, lets know the basic information:
Genetic Connection to Diseases
|
-
Sometimes, a disease may be caused by a genetic mutation (an alter to the person's DNA) in a gene and this gene can be inherited.
-
In some cases, a genetic variant may change the gene, but not actually cause the disease. More gene variants may be needed to cause the disease or to increase the chances of getting the disease (genetic risk factor). (2a)
Perfecto! Now since you know the basics, lets move on and relate this to the topic.
Genetics of Alzheimer's Disease
There are two types of Alzheimer's: Early-onset and late-onset.
Early-Onset Alzheimer's Disease
|
Late-Onset Alzheimer's Disease
In these common cases (developed after age 60), a specific gene still has not been identified as a cause. There is an increased risk related to apolipoptrotein E (apoE) found on chromosome 19. (2a)
|
The research: One of apoE's functions is to transport cholesterol. A researcher, "Susanne Akterin studied mice that had been genetically modified to mimic the effects of apoE4 in humans. The mice were then fed for nine months on a diet rich in fat, sugar and cholesterol, representing the nutritional content of most fast food." (2c)
The results: Akterin found a chemical change within the mice's brain. There was an increase in phosphate groups attached to a Tau protein. "We now suspect that a high intake of fat and cholesterol in combination with genetic factors, such as apoE4, can adversely affect several brain substances, which can be a contributory factor in the development of Alzheimer's." (2c)
Video Clip: Alzheimer's: Is the Cure in the Genes?
*For information about APOE 4, go 5:05 minutes into the clip.
More Genetics!
Previously, it was stated that a mutations on chromosome 21 (beta-amyloid proteins) caused the formation of the amyloid plague, but you may wonder what causes the neurofibrillary tangles?!
Good Question, here's the answer:
The Tau protein's role is to form the neuron’s basic shape and backbone. The mutation of the protein was linked to chromosome 17 where it causes the tau protein to twist. This leads to a build-up of waste and the cell begins to wither and die away. (2b) |
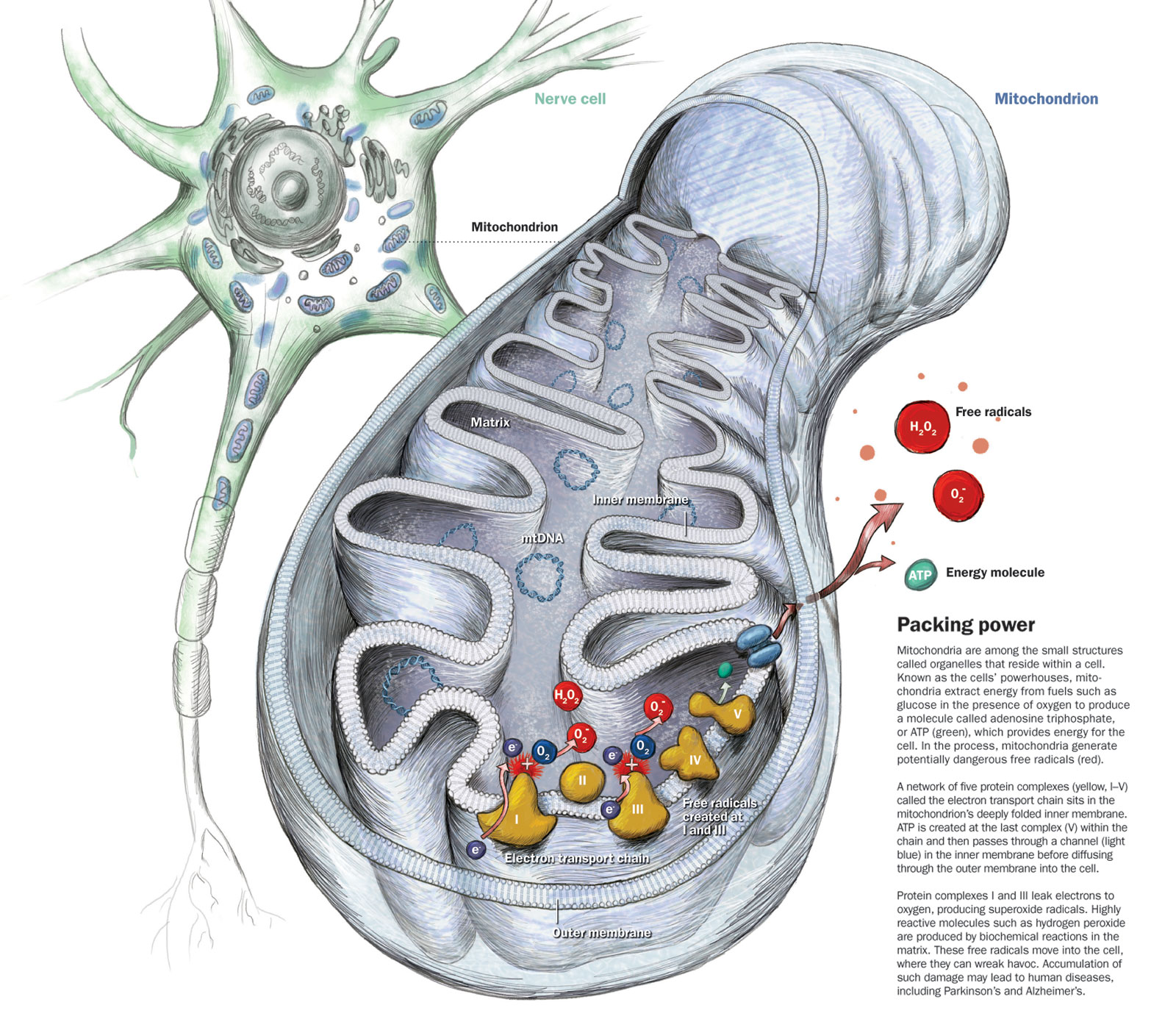
Mitochondria Mutation
The problem: "Mitochondria accumulate mutations in their DNA over a lifetime. As the glitches pile up, they can cause mitochondria to produce less energy or work less efficiently. It's particularly troublesome for the brain and muscles, heavy users of energy. A blackout in cellular every production may also contribute to gray hair, weak bones, and other age-related changes." (2c) What does that mean? Simple! It means: Less energy (ATP) produced by mitochondria leads to abnormal brain function that leads to the beginning signs of Alzheimer's. |